The gut microbiome contains tens of trillions of microorganisms including at least 1000 different species of known bacteria. The mammalian gut microbiome has co-evolved with its hosts for hundreds of millions of years (long before there were mammals) and, therefore, has been extensively involved with a variety of essential activities in the host, e.g. digestion and nutrition, detoxification and body defense, maturation of the host immune system and disease mediation.
You will now be performing your own analysis of microbiome using data obtained from the Bruce-Keller et al., 2015 paper. The data includes sequences from two particularly variable regions of the 16S (V3 and V4) from fecal and cecal samples from donor mice fed either high-fat diets (HFDs) or chow diets (CD). Cecal samples come from the beginning of the large intestine, so sampling both cecal and fecal samples provides information from two distinct microbial populations. The comparison of microbiotic diversity between these two groups will provide information on how high-fat vs normal food consumption may affect GI composition and function and if cognitive and psychiatric impairment correlates with distinct, harmful microbiotic communities.
The data set includes 16S rRNA Amplicon sequences derived from the gut microbiome paper. The dataset includes sequence data from fecal and cecal samples of both donor mice (those who have consumed a high-fat diet, and those who have consumed a normal chow diet) and recipient mice (those receiving either high-fat diets transplanted fecal microbiota or those receiving fecal microbiota from normal chow-fed mice).
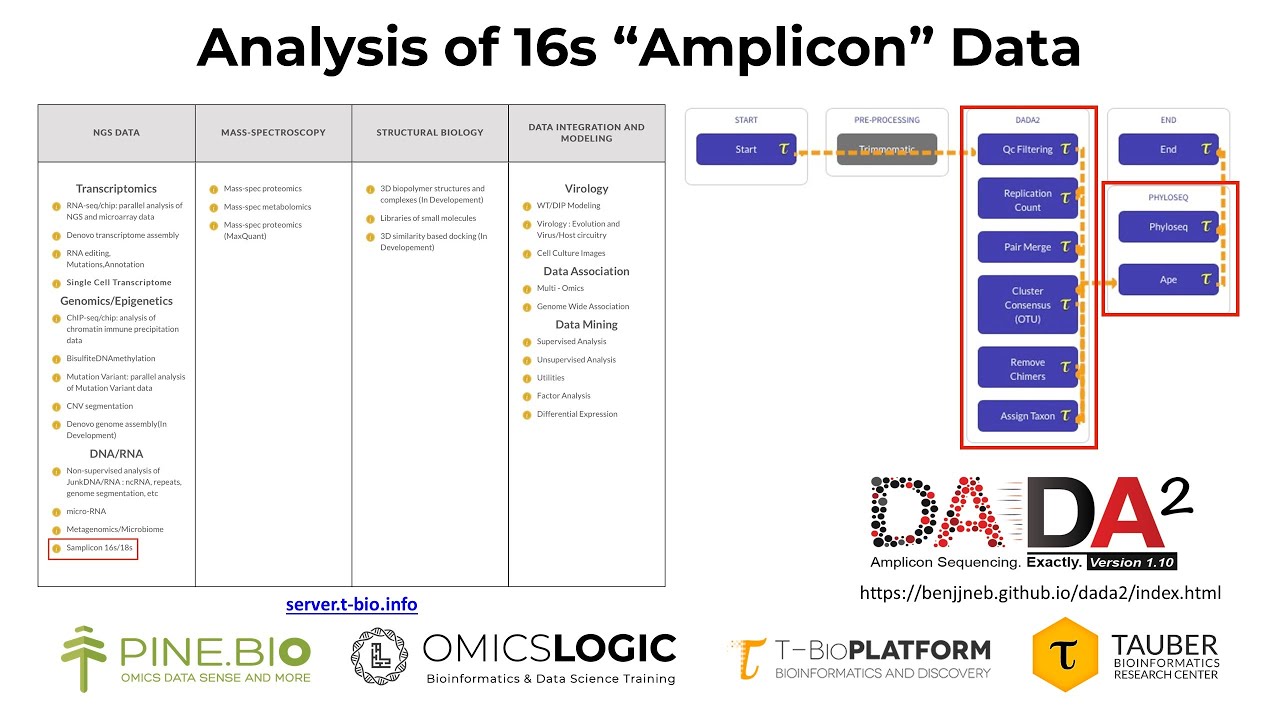
The DADA collection of programs (Callahan et al., 2016) has many different options. Since we are using DNA/RNA amplicon sequences generated by NGS methods, we will select the Amplicon 16S/18S algorithm of the T-Bioinfo platform (Remember, eukaryotic 18S is the same subunit as prokaryotic 16S):