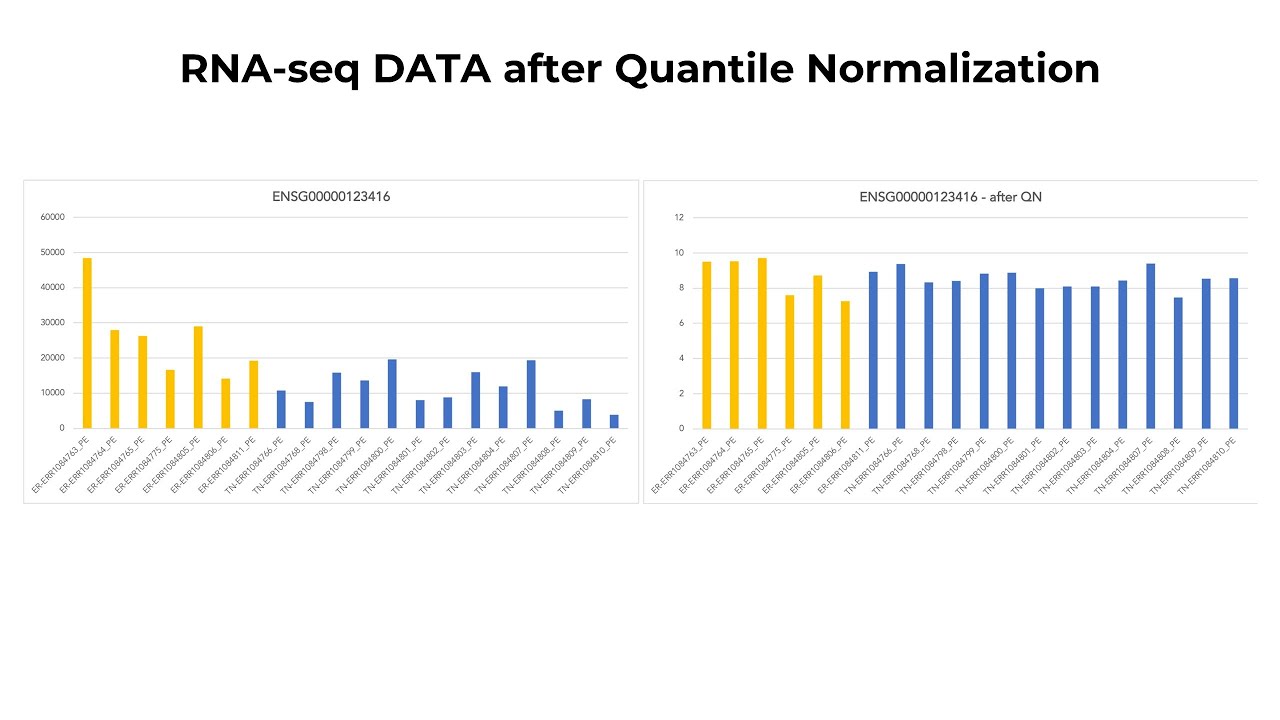
Quantile normalization, and other normalization procedures are important to transform distributions between, and amongst, different samples to have the same distribution. Quantile normalization is a technique of mapping original values to the corresponding quantile of a standard distribution. Here, an estimation of the sequencing depth of an experiment is determined by an upper quartile of its counts.
Comparing quantile values instead of raw values will eliminate differences solely rooted in technical variation, such as the amount of RNA sequenced, sequencing machine type, or even unexplained differences that arise between different technicians following the same protocol. In addition, while normalizing data we will use a log transformation that makes it easier to interpret differences in gene expression.
Expression Levels
The steps (generally speaking) to transform counts to expression levels:
-
Align reads against a set of reference transcript sequences
-
Count the number of reads aligning to each transcript
-
Convert read counts into relative expression levels
Counts to Expression Levels:
RPKM - Reads Per Kilobase per Million mapped reads (used for single-end reads)
FPKM - Fragments per Kilobase per Million mapped reads (used for paired-end reads)
TPM - Transcripts Per Million - TPM is often preferred to RPKM/FPKM because of normalization factor and because TPM is a technology-independent measure (simply a fraction)
RsemExpTable
RSEMExpTable is a module based on the RSEM algorithm that generates an expression table. The table has genes or isoforms as row names and samples as column names. Inside each cell, there is a number corresponding to the level of expression for a given gene in a given sample.
RSEM is an algorithm that quantifies transcript abundances based on the alignment file (sam file). RSEM provides the following result files: gene expression (in FPKM and counts), isoform expression (in FPKM and counts), and alignment statistics. Alignment statistics include summary data on the ways reads were aligned and how many were not aligned at all. More info on RSEM
Sailfish
Sailfish is a computational method for quantifying the abundance of previously annotated RNA isoforms from RNA-seq data. The method entirely avoids mapping reads, a time-consuming step in all current methods, and provides quantification estimates much faster than do existing approaches (typically 20 times faster) without loss of accuracy. Sailfish exemplifies a lightweight algorithm for time-efficient quantification of isoform expression analysis. More info on Sailfish
HTseq
HTSeq is a Python-based script for quantifying gene expression. Given a SAM or BAM alignment file, and a list of features with known genome positions (gtf file), HTSeq calculates the amount of reads overlapping each feature. The algorithm can be used as an alternative to RSEM. More info on HTseq
Link to course material for Quantile Normalization for Gene Expression (RNA- Seq) on T-Bioinfo - https://learn.omicslogic.com/Learn/course-5-transcriptomics/lesson/07-t2-practical-normalization-and-pca-of-gene-expression-data